The Energy Gap: Why Reliable Power Still Eludes Rural Areas
Despite global progress in renewable energy, over 700 million people still live without dependable electricity. Rural communities often rely on unstable grids, diesel generators, or outdated systems that limit productivity and growth.
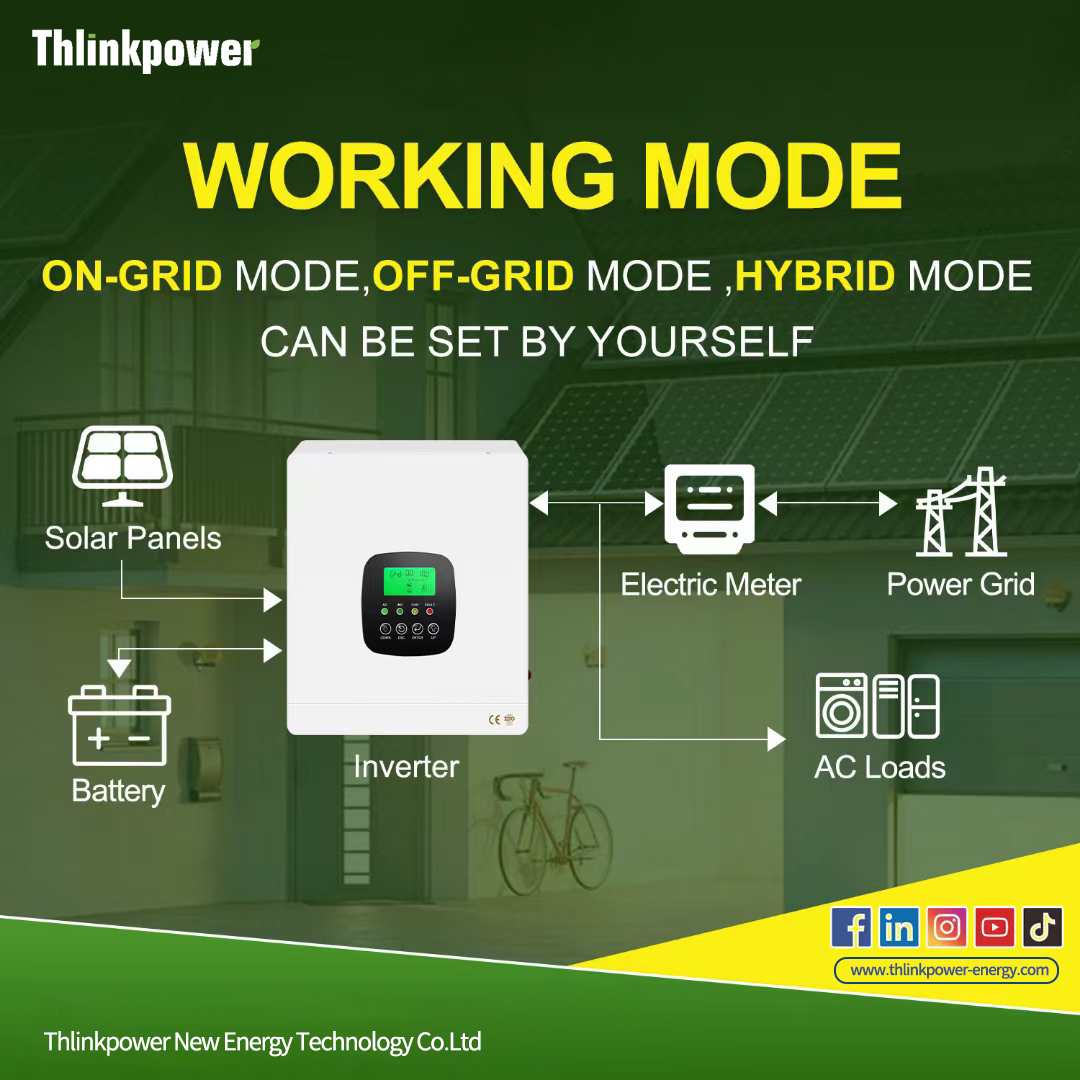
The solution lies in inverters designed for rural electrification — systems capable of converting, stabilizing, and managing renewable energy for off-grid or hybrid applications.
By integrating solar panels, batteries, and local grids, these inverters transform isolated regions into self-sufficient energy ecosystems that power homes, schools, clinics, and small industries.
How Rural Inverter Systems Work
Rural electrification requires more than simply generating electricity — it requires managing it efficiently.
An inverter ensures that the energy produced by solar panels or batteries is converted into stable, usable AC power, even when sunlight or grid supply fluctuates.
| Component | Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Solar Array | Generates DC power from sunlight | Provides sustainable energy source |
| Inverter Unit | Converts DC to AC | Enables use of common household and industrial equipment |
| Battery Storage | Stores excess power for night or cloudy days | Guarantees 24/7 electricity |
| Mini-Grid Controller | Balances local demand and generation | Supports community-level distribution |
This modular design allows rural systems to scale — from powering a single household to supplying an entire village network.
Why Inverters Are Central to Rural Energy Infrastructure
Modern inverters bring intelligence and flexibility to rural power projects.
They ensure not only conversion efficiency but also system reliability in harsh, resource-limited environments.
-
High Conversion Efficiency (up to 98%) — Maximizes limited solar yield.
-
Wide Input Voltage Range — Works even under partial sunlight or variable loads.
-
Off-Grid & Hybrid Modes — Ensures constant power regardless of grid connection.
-
Low Maintenance Design — Reduces service requirements in remote areas.
-
Integrated MPPT & Protection — Prevents system overload and extends battery life.
-
Remote Monitoring — Enables local operators to track performance via GSM or satellite links.
These features allow communities to sustain power generation independently, without needing large utilities.
Comparing Power Models for Rural Electrification
| Power Model | Energy Source | Cost Efficiency | Reliability | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diesel Generator | Fossil fuel | High operational cost | Moderate | Temporary supply |
| Grid Extension | Utility grid | Expensive to deploy | High (if stable grid) | Densely populated areas |
| Solar Inverter System | Solar + Battery | Medium setup, low running cost | High | Scattered villages |
| Hybrid Microgrid | Solar + Battery + Diesel | Medium setup, very high reliability | Very High | Industrial or community-scale electrification |
According to IRENA (2024), inverter-based microgrids can cut the cost of rural power delivery by up to 60% compared to traditional grid extensions while achieving 95–98% uptime in stable sunlight conditions.
Real-World Applications: Where Inverters Empower Communities
-
Village Electrification Projects
-
Powering households, water pumps, and lighting through solar-hybrid systems.
-
-
Rural Health Clinics
-
Ensuring reliable power for medical equipment, refrigeration, and lighting.
-
-
Remote Schools and Training Centers
-
Providing continuous electricity for digital learning and communication.
-
-
Agricultural Cooperatives
-
Running irrigation pumps, grain mills, and cold storage through solar inverters.
-
-
Community Microgrids
-
Connecting multiple homes or businesses with shared hybrid power networks.
-
These projects demonstrate how inverters convert renewable energy into real social and economic impact.
Choosing the Right Inverter for Rural Projects
| Project Scale | Recommended Capacity | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Household System | 1–3 kW | Compact inverter with built-in MPPT |
| Small Village Network | 5–10 kW | Hybrid inverter, dual input for solar + battery |
| Community Microgrid | 15–30 kW | Modular, multi-string inverter with load sharing |
| Rural Industry / Cooperative | 30–100 kW | Three-phase industrial inverter with data logging |
Tip: For rural areas with irregular sunshine, choose hybrid inverters with smart battery management to maximize uptime and prevent power gaps.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Can inverters operate without any grid connection?
Yes, off-grid models work independently using solar and batteries as the main energy sources.
Q2: How long can these systems run without sunlight?
With proper battery sizing, systems can sustain 2–3 days of continuous operation.
Q3: What is the average system lifespan?
Inverters typically last 8–10 years, with solar panels exceeding 20 years.
Q4: Are inverter systems scalable for future growth?
Yes — modular designs allow additional panels or batteries to be added as community demand grows.
Building Energy Access Through Technology
Reliable electricity empowers communities to work, learn, and grow.
Solar inverters make this possible by bridging renewable generation and everyday energy use — turning isolated villages into connected, thriving hubs.
At Thlinksolar, our off-grid and hybrid inverters are engineered for durability, scalability, and low maintenance, ensuring reliable power for remote regions worldwide.
We help governments, NGOs, and private developers build lasting energy solutions for rural progress.
To learn more, visit our homepage or reach out via our contact page.